An In-depth Analysis of Machine Learning
Machine learning is a cutting-edge field of computer science that has witnessed remarkable advancements in recent years. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the core concepts, techniques, and applications of machine learning, as well as delve into its challenges and future prospects.
How it can be defined?
Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence (AI) that focuses on the development of algorithms and models capable of automatically learning and making predictions or decisions based on patterns and data. It enables computers to analyze and interpret complex data without explicit programming instructions, thus allowing them to improve their performance over time.
At the heart of machine learning lies data. Datasets serve as the foundation for training and validating machine learning models. These datasets consist of a collection of examples or instances, each with a set of features or attributes. The quality and quantity of data play a vital role in the effectiveness of machine learning algorithms. Preprocessing techniques such as data cleaning, normalization, and feature selection help ensure the data is suitable for analysis.
Algorithms
Algorithms
Machine learning algorithms are mathematical models that process input data to learn patterns, make predictions, or take actions. These algorithms are designed to automatically adjust their parameters based on the input data and the desired output. Common types of machine learning algorithms include supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning. Each algorithm has its own strengths and limitations, making it suitable for specific tasks.
Training and Testing
Training and Testing
The process of training a machine learning model involves exposing it to labeled examples or historical data to learn patterns and make accurate predictions. The model is iteratively adjusted until it achieves the desired level of performance. Testing the trained model involves evaluating its predictive accuracy on new, unseen data to ensure its generalization capabilities. Techniques such as cross-validation and evaluation metrics like accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score are used to assess model performance.
Unsupervised Learning:
Applications of Machine Learning: Machine learning has found application in various domains, including but not limited to:
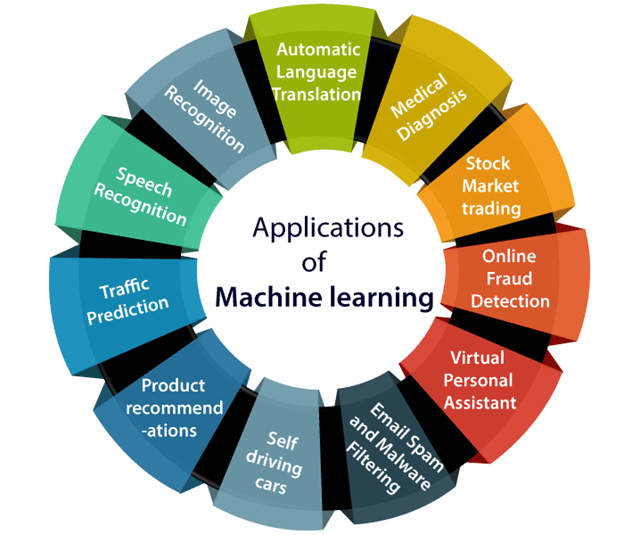
Healthcare: Predictive models for disease diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and drug discovery. Machine learning algorithms can analyze medical images, such as X-rays and MRI scans, to aid in disease detection and diagnosis.
Finance: Fraud detection, risk assessment, and algorithmic trading. Machine learning techniques can analyze vast amounts of financial data to identify fraudulent transactions and assess investment risks.
Marketing: Customer segmentation, recommendation systems, and targeted advertising. Machine learning algorithms can analyze customer behavior and preferences to personalize marketing campaigns and recommend products or services.
Natural Language Processing: Speech recognition, machine translation, and sentiment analysis. Machine learning techniques are used to develop speech recognition systems, language translation tools, and sentiment analysis models that can understand and analyze human language.
Image and Video Analysis: Object recognition, image classification, and video surveillance. Machine learning algorithms can identify and classify objects in images and videos, enabling applications like facial recognition, autonomous vehicles, and surveillance systems.
Challenges and Future Prospects: Despite its significant advancements, machine learning faces several challenges. These include the need for large, high-quality datasets, potential bias in algorithms, interpretability and explainability issues, and ethical considerations regarding privacy and security. Ongoing research focuses on addressing these challenges and developing more robust and transparent machine learning models.
The future of machine learning holds immense potential. Advancements in deep learning, a subfield of machine learning, are enabling breakthroughs in areas such as computer vision, natural language processing, and autonomous systems. The integration of machine learning with other emerging technologies like Internet of Things (IoT) and edge computing opens up new avenues for innovation in areas like smart cities, healthcare monitoring, and personalized user experiences. Continued research, collaboration, and ethical guidelines will shape the responsible development and deployment of machine learning systems.
Conclusion
Now a common question would be how the machine learning models are created?
Well their are various steps involved:
1. Data Collection
- Involves collection of the data from various sources into the data frame.
- By the means of survey, databases.
- Online platforms such as Kaggle, UCI machine learning repository etc.
- This will simply help in the representation of the data.
2. Data Preparation
- Simply known as the cleaning of the data.
- Check the structure of the data, summary of the data.
- Removing the duplicate, unwanted columns, fix the missing values.
- Detecting and fixing the outliers(if necessary).
- Randomize the data, so that the data is not in a particular order.
- Detect some relevant relationships among the features.
- Divide the data frame into training and testing data.
3. Selection of a Model
- As their are different algorithms available for different tasks, get the right one selected.
- Select the model by considering the training data set.
4. Training the Model
- Training of the model is important to get the analysis and the prediction more efficient.
- This will further help in answering the questions of the problems.
5. Evaluate the Model
- Test the model on the testing dataset.
- This data is likely the representative of model performance in the real world.
6. Improving the model Performance
- It's an advance step to boost the model performance which can be done if necessary.
7. Make Prediction Model
- Applying all the previous steps we can create a prediction table or a model.
Types of Machine Learning:
Supervised Learning:
In supervised learning, the algorithm learns from labeled examples, where each example in the training data is associated with a known output. The algorithm generalizes from this labeled data to make predictions on new, unseen inputs. Examples of supervised learning algorithms include linear regression, support vector machines, decision trees, and neural networks. They find applications in various domains, such as predicting housing prices, sentiment analysis, and image classification.
Unsupervised Learning:
Unsupervised learning involves training models on unlabeled data to discover underlying patterns or structures. Unlike supervised learning, there are no pre-defined output labels. Clustering algorithms, such as k-means and hierarchical clustering, group similar data points together based on their features. Dimensionality reduction techniques, such as principal component analysis (PCA) and t-SNE, reduce the number of features while preserving important information. Unsupervised learning is useful for tasks like customer segmentation, anomaly detection, and recommendation systems.
Reinforcement Learning:
Reinforcement Learning:
Reinforcement learning involves an agent that learns to interact with an environment to maximize a reward signal. The agent learns through trial and error, receiving feedback in the form of rewards or penalties based on its actions. Reinforcement learning has been successfully applied in domains such as game playing, robotics, and autonomous systems. Popular algorithms in reinforcement learning include Q-learning and deep reinforcement learning.

Applications of Machine Learning: Machine learning has found application in various domains, including but not limited to:

Healthcare: Predictive models for disease diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and drug discovery. Machine learning algorithms can analyze medical images, such as X-rays and MRI scans, to aid in disease detection and diagnosis.
Finance: Fraud detection, risk assessment, and algorithmic trading. Machine learning techniques can analyze vast amounts of financial data to identify fraudulent transactions and assess investment risks.
Marketing: Customer segmentation, recommendation systems, and targeted advertising. Machine learning algorithms can analyze customer behavior and preferences to personalize marketing campaigns and recommend products or services.
Natural Language Processing: Speech recognition, machine translation, and sentiment analysis. Machine learning techniques are used to develop speech recognition systems, language translation tools, and sentiment analysis models that can understand and analyze human language.
Image and Video Analysis: Object recognition, image classification, and video surveillance. Machine learning algorithms can identify and classify objects in images and videos, enabling applications like facial recognition, autonomous vehicles, and surveillance systems.
Challenges and Future Prospects: Despite its significant advancements, machine learning faces several challenges. These include the need for large, high-quality datasets, potential bias in algorithms, interpretability and explainability issues, and ethical considerations regarding privacy and security. Ongoing research focuses on addressing these challenges and developing more robust and transparent machine learning models.
The future of machine learning holds immense potential. Advancements in deep learning, a subfield of machine learning, are enabling breakthroughs in areas such as computer vision, natural language processing, and autonomous systems. The integration of machine learning with other emerging technologies like Internet of Things (IoT) and edge computing opens up new avenues for innovation in areas like smart cities, healthcare monitoring, and personalized user experiences. Continued research, collaboration, and ethical guidelines will shape the responsible development and deployment of machine learning systems.
Conclusion
Machine learning has revolutionized the way computers process and interpret complex data, enabling them to perform tasks previously thought to be exclusive to human intelligence. With its vast array of applications and potential, machine learning is poised to shape the future across numerous industries, driving innovation and advancement. As the field continues to evolve, further breakthroughs are expected, fueling progress in AI and its real-world impact. Embracing the opportunities and addressing the challenges will pave the way for a future where machine learning enhances human capabilities and improves society as a whole.

Comments
Post a Comment